我们也听说过Java的面向接口编程,即官方提供一系列接口给第三方去实现,然后利用接口去调用第三方的实现类,如果有多个第三方都实现了该接口,那么对于官方来说,都可以利用该接口调用这些第三方的实现类,且不关心第三方是如何具体实现的,我只管调用就行了。
JDBC正是利用了接口编程思想,JDBC只是接口,JDBC驱动才是该接口的实现类,每个数据库都有其对应的JDBC驱动,没有JDBC驱动是没有办法连接数据库的!
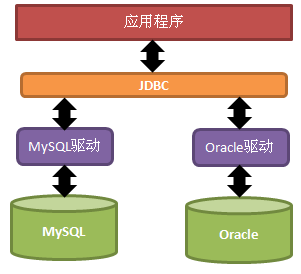
JDBC接口核心的API
Driver接口
每个驱动程序必须实现的接口,每个驱动程序都应该提供一个实现 Driver 接口的类。 它有一个很重要的方法:
Connection connect(String url,Properties info) throws SQLException
此方法是连接数据库的方法,并返回一个与数据库已连接的连接对象;参数url表示连接数据库的地址,其写法:jdbc协议:数据库子协议://主机:端口/数据库,如MySql的数据库连接地址可以写成:
url:jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
info封装了连接数据库的用户名和密码。也就是说该方法是Java与数据库连接的桥梁。
DriverManager类
顾名思义,这是数据库驱动的管理类,负责管理所有注册的驱动程序,主要有如下方法:
static void registerDriver(Driver driver);// 这是注册驱动的方法
static Connection getConnection(String url, String user, String password);// 获取连接对象
此方法内部调用了驱动程序实现了Driver接口的Connection connect(String url,Properties info)方法,从而获得连接对象。
Connection接口
表示java连接数据库的对象,并可执行sql语句并返回结果,其主要方法:
Statement createStatement();// 创建Statement对象
PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql);// 创建PreparedStatement对象
第二个方法用得最多,因为它可以预编译sql语句,这大大节省了数据库的开销。
而PreparedStatement接口的主要方法如下:
int executeUpdate(); // 执行预编译的更新sql语句(DDL,DML)
ResultSet executeQuery();// 执行预编译的查询sql语句(DQL)
获取连接对象源码分析
DriverManager源码
DriverManager驱动管理类可以注册所有实现了JDBC接口的数据库驱动,并通过DriverManager.getConnection()方法驱动获取与之相对应的数据库的连接对象,这就是面向接口编程的体现。
我们从入口DriverManager.getConnection()开始进入驱动源码的世界:
publicclass DriverManager {
// 此处省略部分代码
public static Connection getConnection(String url,
String user, String password) throws SQLException {
java.util.Properties info = new java.util.Properties();
// 封装用户名和密码
if (user != null) {// 用户名
info.put("user", user);
}
if (password != null) { // 密码
info.put("password", password);
}
return (getConnection(url, info, Reflection.getCallerClass()));
}
private static Connection getConnection(
String url, java.util.Properties info, Class<?> caller) throws SQLException {
// 获取类加载器
ClassLoader callerCL = caller != null ? caller.getClassLoader() : null;
// 同步块,获取当前线程的类加载器
synchronized(DriverManager.class) {
if (callerCL == null) {
callerCL = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
}
}
// 此处省略部分代码
// 这里遍历的是在registerDriver(Driver driver)方法中注册的驱动对象
// 每个DriverInfo包含了驱动对象和其信息
for(DriverInfo aDriver : registeredDrivers) {
// 判断是否为当前线程类加载器加载的驱动类
if(isDriverAllowed(aDriver.driver, callerCL)) {
try {
println(" trying " + aDriver.driver.getClass().getName());
// 获取连接对象,这里调用了Driver的父类的方法
Connection con = aDriver.driver.connect(url, info);
if (con != null) {
// 打印连接成功信息
println("getConnection returning " + aDriver.driver.getClass().getName());
// 返回连接对像
return (con);
}
} catch (SQLException ex) {
if (reason == null) {
reason = ex;
}
}
} else {
println(" skipping: " + aDriver.getClass().getName());
}
}
// 此处省略部分代码
}
}
MySql Driver驱动源码
MySql的Driver实现类(此类主要任务是注册驱动):
public class Driver extends NonRegisteringDriver implements java.sql.Driver {
//静态代码块
static {
try {
java.sql.DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver());// 注册驱动
} catch (SQLException E) {
throw new RuntimeException("Can't register driver!");
}
}
}
注:由于mysql数据库驱动类com.mysql.jdbc.Driver在获取连接对象之前要加载到jvm中,所以在获取对象之前驱动类已注册到驱动管理类中了,加载驱动如下:
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
执行这行代码后,驱动类的静态代码块随之执行,也就把驱动注册了。但是在高版本的MySql已经不需要执行这句代码了,把驱动类名写在相应的配置文件里,当jvm加载DriverManager类时会自动执行类中静态代码块加载驱动,源码如下:
private DriverManager(){}
static {
loadInitialDrivers();
println("JDBC DriverManager initialized");
}
从上面可看出,DriverManager初始化时会执行静态代码块中的代码,loadInitialDrivers()是用于加载外部实现的驱动类的方法。
其父类(此类主要任务是实现连接细节):
public class NonRegisteringDriver implements java.sql.Driver {
// 此处省略部分代码
// 实现connect方法
public java.sql.Connection connect(String url, Properties info) throws SQLException {
// 此处省略部分代码
try {
// 这里获取具体的链接 类是ConnectionImpl,调用其getInstance方法创建并返回Connection对象
Connection newConn = com.mysql.jdbc.ConnectionImpl.getInstance(
host(props), port(props), props, database(props), url);
return newConn;
} catch (SQLException sqlEx) {
// 此处省略部分代码
} catch (Exception ex) {
// 此处省略部分代码
}
}
// 此处省略部分代码
}
MySql connection接口实现源码
mysql的ConnectionImpl类实现了Connection接口,getInstance方法的细节如下:
// 参数有: 主机 端口号 properties database url
protected static Connection getInstance(String hostToConnectTo, int portToConnectTo, Properties info, String databaseToConnectTo, String url)
throws SQLException {
// 调用util 类的方法判断,驱动类是否能够找到
// 创建ConnectionImpl对象
if (!Util.isJdbc4()) {
return new ConnectionImpl(hostToConnectTo, portToConnectTo, info, databaseToConnectTo, url);
}
return (Connection) Util.handleNewInstance(JDBC_4_CONNECTION_CTOR, new Object[] { hostToConnectTo, Integer.valueOf(portToConnectTo), info,
databaseToConnectTo, url }, null);
}
ConnectionImpl类构造方法:
public ConnectionImpl(String hostToConnectTo, int portToConnectTo, Properties info, String databaseToConnectTo, String url) throws SQLException {
this.connectionCreationTimeMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (databaseToConnectTo == null) {
databaseToConnectTo = "";
}
// Stash away for later, used to clone this connection for Statement.cancel and Statement.setQueryTimeout().
//
this.origHostToConnectTo = hostToConnectTo; // host
this.origPortToConnectTo = portToConnectTo; //port
this.origDatabaseToConnectTo = databaseToConnectTo; //数据库名
try {
Blob.class.getMethod("truncate", new Class[] { Long.TYPE });
this.isRunningOnJDK13 = false;
} catch (NoSuchMethodException nsme) {
this.isRunningOnJDK13 = true;
}
this.sessionCalendar = new GregorianCalendar();
this.utcCalendar = new GregorianCalendar();
this.utcCalendar.setTimeZone(TimeZone.getTimeZone("GMT"));
//
// Normally, this code would be in initializeDriverProperties, but we need to do this as early as possible, so we can start logging to the 'correct'
// place as early as possible...this.log points to 'NullLogger' for every connection at startup to avoid NPEs and the overhead of checking for NULL at
// every logging call.
//
// We will reset this to the configured logger during properties initialization.
//
this.log = LogFactory.getLogger(getLogger(), LOGGER_INSTANCE_NAME, getExceptionInterceptor());
this.openStatements = new HashMap<Statement, Statement>();
if (NonRegisteringDriver.isHostPropertiesList(hostToConnectTo)) {
Properties hostSpecificProps = NonRegisteringDriver.expandHostKeyValues(hostToConnectTo);
Enumeration<?> propertyNames = hostSpecificProps.propertyNames();
while (propertyNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String propertyName = propertyNames.nextElement().toString();
String propertyValue = hostSpecificProps.getProperty(propertyName);
info.setProperty(propertyName, propertyValue);
}
} else {
if (hostToConnectTo == null) {
this.host = "localhost";
this.hostPortPair = this.host + ":" + portToConnectTo;
} else {
this.host = hostToConnectTo;
if (hostToConnectTo.indexOf(":") == -1) {
this.hostPortPair = this.host + ":" + portToConnectTo;
} else {
this.hostPortPair = this.host;
}
}
}
// 获取了所有链接数据库需要的参数
this.port = portToConnectTo;
this.database = databaseToConnectTo;
this.myURL = url;
this.user = info.getProperty(NonRegisteringDriver.USER_PROPERTY_KEY);
this.password = info.getProperty(NonRegisteringDriver.PASSWORD_PROPERTY_KEY);
if ((this.user == null) || this.user.equals("")) {
this.user = "";
}
if (this.password == null) {
this.password = "";
}
this.props = info;
initializeDriverProperties(info);
// We store this per-connection, due to static synchronization issues in Java's built-in TimeZone class...
this.defaultTimeZone = TimeUtil.getDefaultTimeZone(getCacheDefaultTimezone());
this.isClientTzUTC = !this.defaultTimeZone.useDaylightTime() && this.defaultTimeZone.getRawOffset() == 0;
if (getUseUsageAdvisor()) {
this.pointOfOrigin = LogUtils.findCallingClassAndMethod(new Throwable());
} else {
this.pointOfOrigin = "";
}
try {
this.dbmd = getMetaData(false, false);
// 进行数据库的链接
initializeSafeStatementInterceptors();
// 创建io流
createNewIO(false);
unSafeStatementInterceptors();
} catch (SQLException ex) {
// 此处省略部分代码
} catch (Exception ex) {
// 此处省略部分代码
}
NonRegisteringDriver.trackConnection(this);
}
创建连接的具体实现就在createNewIO();方法中,继续往下:
public void createNewIO(boolean isForReconnect) throws SQLException {
synchronized(this.getConnectionMutex()) {
Properties mergedProps = this.exposeAsProperties(this.props);
if(!this.getHighAvailability()) {
// 尝试一次链接
this.connectOneTryOnly(isForReconnect, mergedProps);
} else {
// 尝试多次链接
this.connectWithRetries(isForReconnect, mergedProps);
}
}
}
无论调用一次还是多次链接,都会调用ConnectionImpl类中获取链接I/O流的核心代码:
// 链接核心代码
private void coreConnect(Properties mergedProps) throws SQLException, IOException {
int newPort = 3306;
String newHost = "localhost";
String protocol = mergedProps.getProperty("PROTOCOL");
if(protocol != null) {
if("tcp".equalsIgnoreCase(protocol)) {
newHost = this.normalizeHost(mergedProps.getProperty("HOST"));
newPort = this.parsePortNumber(mergedProps.getProperty("PORT", "3306"));
} else if("pipe".equalsIgnoreCase(protocol)) {
this.setSocketFactoryClassName(NamedPipeSocketFactory.class.getName());
String path = mergedProps.getProperty("PATH");
if(path != null) {
mergedProps.setProperty("namedPipePath", path);
}
} else {
newHost = this.normalizeHost(mergedProps.getProperty("HOST"));
newPort = this.parsePortNumber(mergedProps.getProperty("PORT", "3306"));
}
} else {
String[] parsedHostPortPair = NonRegisteringDriver.parseHostPortPair(this.hostPortPair);
newHost = parsedHostPortPair[0];
newHost = this.normalizeHost(newHost);
if(parsedHostPortPair[1] != null) {
newPort = this.parsePortNumber(parsedHostPortPair[1]);
}
}
this.port = newPort;
this.host = newHost;
this.sessionMaxRows = -1;
// 通过ip, 端口等属性获取链接数据库得IO流,
this.io = new MysqlIO(newHost, newPort, mergedProps, this.getSocketFactoryClassName(), this.getProxy(), this.getSocketTimeout(), this.largeRowSizeThreshold.getValueAsInt());
this.io.doHandshake(this.user, this.password, this.database);
if(this.versionMeetsMinimum(5, 5, 0)) {
this.errorMessageEncoding = this.io.getEncodingForHandshake();
}
}
在这里可以发现,coreConnect()方法通过创建MysqlIO类获取了链接数据库的io流,而具体的socket 是调用了socketFactory 这个接口的实现类StandardSocketFactory 这个类的实例的connect 方法获取了一个指定的IP ,Port的socket 链接。
到这里,我们发现获取MySql链接实通过DriverManager.getConnection()–>调用com.mysql.jdbc.Driver驱动–>创建Connection实现类,并通过指定的IP,端口获取与数据库的Socket链接。
参考原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/qh_java/article/details/50390038
