Mybatis 是一个「面向 sql」的持久层框架,它可实现动态拼装 sql,极其灵活,同时避免了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码和手动设置参数以及获取结果集,其插件机制允许在已映射语句执行过程中的某一点进行拦截调用等等,让我忍不住想要撸一撸它的源码。
我们都知道 Mapper 是一个接口,它的每个方式是我们与数据库交互的入口,每个 Mapper 都有与之相对应的一个 XML 文件,我们可以在 XML 里面自由快活地写 sql,当然我们也可以用注解的形式写在接口方法上,但终究还是没 XML 灵活,那么问题来了,Mybatis 是如何注册与绑定 Mapper 的呢?下面我带你揭开这个神秘的面纱。
首先我们来看看用 Mybatis 执行 sql 的两种方法
- 直接操作 SqlSession 方法
public User findUserById(Integer userId) {
SqlSession sqlSession = MyBatisSqlSessionFactory.getSqlSession();
try {
// namespace + statementId
return sqlSession.selectOne("com.objcoding.mybatis.UserMapper.findUserById", userId);
} finally {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
- 通过 Mapper 接口
public User findUserById(Integer userId) {
SqlSession sqlSession = MyBatisSqlSessionFactory.getSqlSession();
try {
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
return userMapper.findUserById(userId);
} finally {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
public class UserMapper {
User findUserById(@Param("userId") String userId);
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.objcoding.mybatis.UserMapper">
<select id="findUserById" resultType="com.objcoding.mybatis.User">
SELECT * FROM user WHERE user_id=#{userId}
</select>
</mapper>
很明显,第二种方法可以大大降低了手工写 namespace 出现错误的概率,且用 Mapper 可以直接操作方法来实现数据链接,看起来优雅很多。
那么 Mapper 是如何示例化的,它是通过 Java 动态代理生成的一个代理类,并与 sqlSession 关联一起,看如下图:
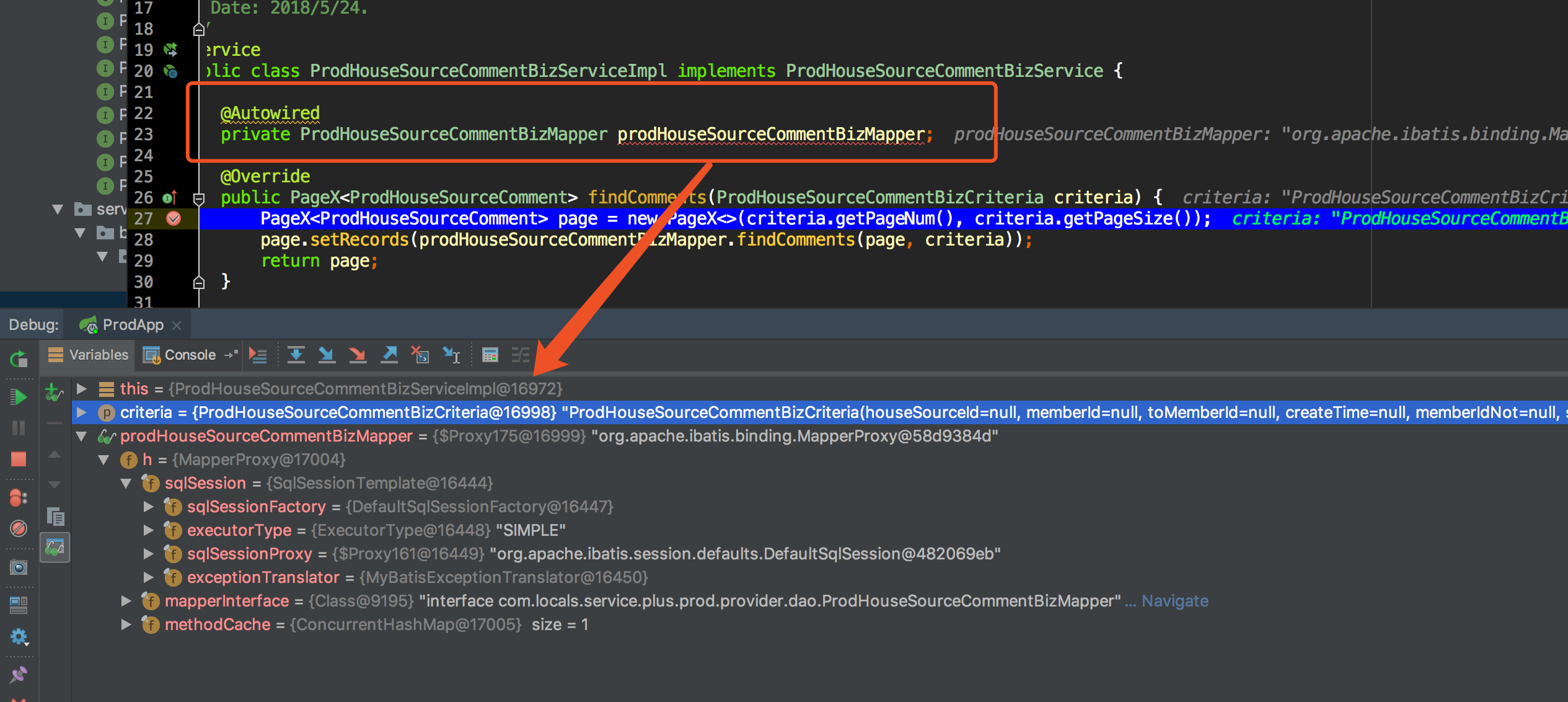
看得出来,此时的 Mapper 是 Spring Bean 容器里面的一个 Bean,它是一个代理类,那么这个代理类的生成过程是怎样的呢?下面带你一起看看 mybatis 源码。
- 创建一个 SqlSessionFactory 实例并注入 Bean 容器中:
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory() throws Exception {
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver resolver = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
// 此处省略部分代码
bean.setMapperLocations(resolver.getResources("classpath*:com/**/*Mapper.xml"));//
return bean.getObject();
}
- bean.getObject():
@Override
public SqlSessionFactory getObject() throws Exception {
if (this.sqlSessionFactory == null) {
afterPropertiesSet();
}
return this.sqlSessionFactory;
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
// 此处省略部分代码
this.sqlSessionFactory = buildSqlSessionFactory();
}
- sqlSessionFactory.buildSqlSessionFactory()
protected SqlSessionFactory buildSqlSessionFactory() throws Exception {
Configuration configuration;
// 此处省略部分代码
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory =this.sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(configuration);
// 此处省略部分代码
if (!isEmpty(this.mapperLocations)) {
// 此处省略部分代码
try {
/**
* 解析 mapperLocation 中的 xml 文件,并生成一个 XMLMapperBuilder
*/
XMLMapperBuilder xmlMapperBuilder = new XMLMapperBuilder(mapperLocation.getInputStream(), configuration, mapperLocation.toString(), configuration.getSqlFragments());
// 执行解析
xmlMapperBuilder.parse();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new NestedIOException("Failed to parse mapping resource: '" + mapperLocation + "'", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
// 此处省略部分代码
return sqlSessionFactory;
}
XMLMapperBuilder 这个类主要是用于解析 mybatis 中的 < mapper >标签里边的内容,功能与 XMLConfigBuilder 类似,都是解析 xml 内容,从源码看,拿到 mapperLocation 的输入流和 configuration 来初始化本身,mapperLocation 即是我们从配置文件配的 mapper XML 地址的封装类
- XMLMapperBuilder.parse()
public void parse() {
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
/**
* 1.解析xml中的节点信息,并生成 MappedStatement
*/
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
/**
* 2.根据 Namespace 绑定 Mapper,也会解析 Mapper 注解中的信息生成 MappedStatement
*/
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
parsePendingResultMaps();
parsePendingCacheRefs();
parsePendingStatements();
}
该方法即是 Mapper xml 节点解析与 Mapper 注解解析以及注册于绑定的入口。
- XMLMapperBuilder.configurationElement(XNode context)
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.equals("")) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
// 解析 xml 中的 sql 片段
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
// 解析与 Mapper 方法对应的 sql
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
该方法将 Mapper xml 的各个节点进行读取,并生成 MapperStatement 添加到 Configuration 中,根据 Namespace 对 Mapper 进行注册绑定。
- XMLMapperBuilder.bindMapperForNamespace()
private void bindMapperForNamespace() {
// 获取 mapper.xml 中 namespace 的 mapper 类名
String namespace = builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace();
if (namespace != null) {
Class<?> boundType = null;
try {
// 根据类名加载 class 对象
boundType = Resources.classForName(namespace);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
//ignore, bound type is not required
}
if (boundType != null) {
if (!configuration.hasMapper(boundType)) {
configuration.addLoadedResource("namespace:" + namespace);
// 绑定操作
configuration.addMapper(boundType);
}
}
}
}
该方法找到 mapper.xml 的 mapper 类名,再根据类名找到加载 class 对象,最后进行绑定操作:
- MapperRegistry.addMapper()
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
// mapper 与 MapperProxyFactory 进行映射
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<T>(type));
// mapper注解构建器
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
// 解析
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
MapperRegistry 类是一个 Mapper 类注册工厂,把与 MapperProxyFactory 映射过的 Mapper 类添加到它的属性 knownMappers 中;
- MapperProxyFactory 类是 生产 Mapper 代理类的工厂,用 Java 动态代理实现:
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<Method, MapperMethod>();
public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
public Class<T> getMapperInterface() {
return mapperInterface;
}
public Map<Method, MapperMethod> getMethodCache() {
return methodCache;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
}
从方法 newInstance 方法终于看出来了,从这里生产出来的 Mapper 代理类,是与 SqlSession 关联起来的,我们继续往下看:
- MapperProxy.invoke()
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) {
return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
- mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args)
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
// 此处省略部分代码
}
return result;
}
谜底揭开了,我们每次调用 Mapper 的方法,其实是调用这个 execute 方法,而这个方法实则在调用 SqlSession 的方法与数据库交互,通过cachedMapperMethod(method);这个方法拿到执行 sql 相关信息,其实它就是从 congfiguration 类的属性 MappedStatement 中获取的:
- MapperMethod.resolveMappedStatement()
private MappedStatement resolveMappedStatement(Class<?> mapperInterface, String methodName, Class<?> declaringClass, Configuration configuration) {
String statementId = mapperInterface.getName() + "." + methodName;
if (configuration.hasStatement(statementId)) {
// 获取 MappedStatement
return configuration.getMappedStatement(statementId);
} else if (mapperInterface.equals(declaringClass)) {
return null;
}
for (Class<?> superInterface : mapperInterface.getInterfaces()) {
if (declaringClass.isAssignableFrom(superInterface)) {
MappedStatement ms = resolveMappedStatement(superInterface, methodName,
declaringClass, configuration);
if (ms != null) {
return ms;
}
}
}
return null;
}
MappedStatement 类是保存 Mapper 一个执行方法映射的一个节点(select/insert/delete/update),包括配置的 sql,sql 的 id、缓存信息、resultMap、parameterType、resultType 等重要配置内容。
Mybatis 是如何将Mapper 中的方法节点信息添加到 configuration 的 MappedStatement 属性中呢?我们回到MapperRegistry.addMapper()这个方法,看看 MapperAnnotationBuilder 最后的解析:
- MapperAnnotationBuilder.parse()
public void parse() {
String resource = type.toString();
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
// 优先进行 xml 语句的解析,
loadXmlResource();
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
assistant.setCurrentNamespace(type.getName());
parseCache();
parseCacheRef();
Method[] methods = type.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
try {
// issue #237
if (!method.isBridge()) {
// 解析一个方法生成对应的 MapperedStatement 对象
parseStatement(method);
}
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new MethodResolver(this, method));
}
}
}
parsePendingMethods();
}
MapperAnnotationBuilder.parse() 该方法最终目的是将 sql 与 mapper 方法等相关信息封装成一个 MapperStatement,并添加到 Configuration 中,以便执行 Mapper 代理类可以找到相对应的 MapperStatement 拿出对应的信息,再根据这些信息调用 SqlSession。
- MapperAnnotationBuilder.parseStatement(Method method)
void parseStatement(Method method) {
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = getParameterType(method);
// 加载注解 @Lang 的 LanguageDriver
LanguageDriver languageDriver = getLanguageDriver(method);
/**
* 从方法获取 sql 资源类
*/
SqlSource sqlSource = getSqlSourceFromAnnotations(method, parameterTypeClass, languageDriver);
if (sqlSource != null) {
// 此处省略部分代码
/**
* 将 MappedStatement 添加到 Configuration 中
*/
assistant.addMappedStatement(mappedStatementId,sqlSource,statementType,sqlCommandType, fetchSize,timeout,null,parameterTypeClass,resultMapId,getReturnType(method),resultSetType,flushCache,useCache,false,keyGenerator,keyProperty,keyColumn,null,languageDriver,options != null ? nullOrEmpty(options.resultSets()) : null);
}
}
该方法目的是将 Mapper 中的注解信息生成一个 MapperStatement,并将 MapperStatement 添加到 Configuration 中。
从以上源码分析过程得出:Mybatis 在生成一个 SqlSessionFactory 的过程中,主要干了两件事情:
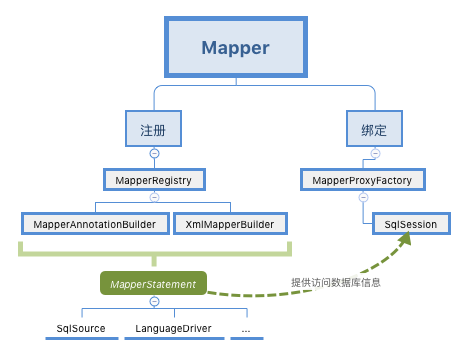
- 注册:将 Mapper xml 中的节点信息和 Mapper 类中的注解信息与 Mapper 类的方法一一对应,每个方法对应生成一个 MapperStatement,并添加到 Configuration 中;
- 绑定:根据 Mapper xml 中的 namespace 生成一个 Mapper class 对象,并与一个 MapperProxyFactory 代理工厂对应,用于 Mapper 代理对象的生成。
最后附上一张简陋的脑图: