向大家提个问题: RocketMQ 消息消费进度是如何提交的,并发消费的时候,一次从 一个队列拉 32 条消息,这 32 条消息会提交到线程池中处理,如果偏移量 m5 比 m4 先执行完成,消息消费后,提交的消费进度是哪个?是提交消息m5的偏移量? 下面跟着我的节奏,撸一波源码。
RocketMQ 每次拉取完消息都会将消息存储到 PullRequest 对象中的 ProcessQueue 中:
org.apache.rocketmq.client.consumer.PullCallback#onSuccess
boolean dispathToConsume = processQueue.putMessage(pullResult.getMsgFoundList());
接着将消息放进消费线程中去执行:
org.apache.rocketmq.client.consumer.PullCallback#onSuccess
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.consumeMessageService.submitConsumeRequest(//
pullResult.getMsgFoundList(), //
processQueue, //
pullRequest.getMessageQueue(), //
dispathToConsume);
ConsumeMessageService 类实现消息消费的逻辑,它有两个实现类:
// 并发消息消费逻辑实现类
org.apache.rocketmq.client.impl.consumer.ConsumeMessageConcurrentlyService;
// 顺序消息消费逻辑实现类
org.apache.rocketmq.client.impl.consumer.ConsumeMessageOrderlyService;
这里我们只分析并发消费:
org.apache.rocketmq.client.impl.consumer.ConsumeMessageConcurrentlyService#submitConsumeRequest
ConsumeRequest consumeRequest = new ConsumeRequest(msgThis, processQueue, messageQueue);
try {
this.consumeExecutor.submit(consumeRequest);
} catch (RejectedExecutionException e) {
// ...
}
将消息消费任务封装成 ConsumeRequest 对象,然后将其交给消费线程池中去执行。
org.apache.rocketmq.client.impl.consumer.ConsumeMessageConcurrentlyService.ConsumeRequest#run:
if (!processQueue.isDropped()) {
ConsumeMessageConcurrentlyService.this.processConsumeResult(status, context, this);
} else {
log.warn("processQueue is dropped without process consume result. messageQueue={}, msgs={}", messageQueue, msgs);
}
ConsumeRequest 是一个实现了 Runnable 的类,因此消息消费的核心逻辑都写在了 run 方法中,如上代码是提交已消费位移的逻辑,当 ProcessQueue 没有被丢弃,则进行已消费位移的提交。
org.apache.rocketmq.client.impl.consumer.ConsumeMessageConcurrentlyService#processConsumeResult
// 移除已消费的消息,并返回已消费的
long offset = consumeRequest.getProcessQueue().removeMessage(consumeRequest.getMsgs());
if (offset >= 0 && !consumeRequest.getProcessQueue().isDropped()) {
this.defaultMQPushConsumerImpl.getOffsetStore().updateOffset(consumeRequest.getMessageQueue(), offset, true);
}
移除已消费的位移,并返回最小位移量,如果最小位移量大于 0,并且 ProcessQueue 没有被丢弃,则更新本地缓存,
org.apache.rocketmq.client.impl.consumer.ProcessQueue#removeMessage
public long removeMessage(final List<MessageExt> msgs) {
long result = -1;
final long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
this.lockTreeMap.writeLock().lockInterruptibly();
this.lastConsumeTimestamp = now;
try {
if (!msgTreeMap.isEmpty()) {
result = this.queueOffsetMax + 1;
int removedCnt = 0;
// 移除已消费的消息
for (MessageExt msg : msgs) {
MessageExt prev = msgTreeMap.remove(msg.getQueueOffset());
if (prev != null) {
removedCnt--;
}
}
// 消息总量累加
msgCount.addAndGet(removedCnt);
// 返回消息容器中最小元素 key
if (!msgTreeMap.isEmpty()) {
result = msgTreeMap.firstKey();
}
}
} finally {
this.lockTreeMap.writeLock().unlock();
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
log.error("removeMessage exception", t);
}
return result;
}
以上方法就是解答文章开头问题的关键,由于该方法是各个消费线程并发执行,因此需要对其进行加锁操作,msgTreeMap 是 ProcessQueue 的消息容器,它的格式如下:
private final TreeMap<Long, MessageExt> msgTreeMap = new TreeMap<>();
它是一个 TreeMap 结构,key 为消息位移,value 为消息数据,消息容器中,消息可以按照位移进行排序,那也就意味着,当消息消费完,只需要在消息容器中移除即可,然后返回消息容器中最小元素(最小位移),如下:
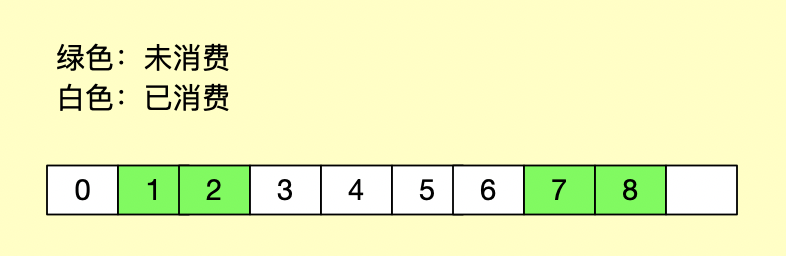
由于消息是按照位移进行排序,因此我们只需移除已消费的消息,并且确保不会将未消费的位移提交,就可避免了位移大的消息先消费导致消息丢失的问题了。
接下来我们继续看
org.apache.rocketmq.client.consumer.store.RemoteBrokerOffsetStore#updateOffset:
public void updateOffset(MessageQueue mq, long offset, boolean increaseOnly) {
if (mq != null) {
AtomicLong offsetOld = this.offsetTable.get(mq);
if (null == offsetOld) {
offsetOld = this.offsetTable.putIfAbsent(mq, new AtomicLong(offset));
}
if (null != offsetOld) {
if (increaseOnly) {
MixAll.compareAndIncreaseOnly(offsetOld, offset);
} else {
offsetOld.set(offset);
}
}
}
}
offsetTable 为本地位移缓存容器,它的结构如下:
private ConcurrentMap<MessageQueue, AtomicLong> offsetTable = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
它是一个 ConcurrentMap,一个线程安全容器,key 为 MessageQueue,value 为当前 MessageQueue 的消费位移,从源码看出,当前消费位移的更新,只能是递增更新。
在更新完本地缓存之后,RocketMQ 是如何将其提交到 broker 的呢?
org.apache.rocketmq.client.impl.factory.MQClientInstance#startScheduledTask:
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
MQClientInstance.this.persistAllConsumerOffset();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("ScheduledTask persistAllConsumerOffset exception", e);
}
}
}, 1000 * 10, this.clientConfig.getPersistConsumerOffsetInterval(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
以上,消费者在启动的时候,开启了一个定时任务,定时将本地缓存提交到broker。
org.apache.rocketmq.client.consumer.store.RemoteBrokerOffsetStore#persistAll:
// 参数mqs是当前分配的队列
public void persistAll(Set<MessageQueue> mqs) {
if (null == mqs || mqs.isEmpty())
return;
final HashSet<MessageQueue> unusedMQ = new HashSet<MessageQueue>();
if (!mqs.isEmpty()) {
// 遍历位移缓存容器
for (Map.Entry<MessageQueue, AtomicLong> entry : this.offsetTable.entrySet()) {
MessageQueue mq = entry.getKey();
AtomicLong offset = entry.getValue();
if (offset != null) {
// 位移缓存容器包含在当前分配队列,则进行消费位移提交
if (mqs.contains(mq)) {
try {
// 提交消费位移
this.updateConsumeOffsetToBroker(mq, offset.get());
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("updateConsumeOffsetToBroker exception, " + mq.toString(), e);
}
} else {
unusedMQ.add(mq);
}
}
}
}
// 将未分配的队列从位移缓存中移除
if (!unusedMQ.isEmpty()) {
for (MessageQueue mq : unusedMQ) {
this.offsetTable.remove(mq);
log.info("remove unused mq, {}, {}", mq, this.groupName);
}
}
}
最终会调用以上方法,RocketMQ 会从重平衡那里获取当前消费者已分配的队列,如果位移缓存容器包含在当前分配队列,则进行消费位移提交,否则将从位移缓存容器中移除。
broker 端处理:
org.apache.rocketmq.broker.offset.ConsumerOffsetManager#commitOffset
private void commitOffset(final String clientHost, final String key, final int queueId, final long offset) {
ConcurrentMap<Integer, Long> map = this.offsetTable.get(key);
if (null == map) {
map = new ConcurrentHashMap<Integer, Long>(32);
map.put(queueId, offset);
this.offsetTable.put(key, map);
} else {
Long storeOffset = map.put(queueId, offset);
if (storeOffset != null && offset < storeOffset) {
log.warn("[NOTIFYME]update consumer offset less than store. clientHost={}, key={}, queueId={}, requestOffset={}, storeOffset={}", clientHost, key, queueId, offset, storeOffset);
}
}
}
以上,offsetTable 为 broker 端的消费位移缓存容器,它的结构如下:
private ConcurrentMap<String/* topic@group */, ConcurrentMap<Integer, Long>> offsetTable =
new ConcurrentHashMap<>(512);
它同样是一个 ConcurrentMap,一个线程安全容器,key 为的形式为 “topic@group”,value 也是一个 ConcurrentMap 它的 key 为 queueId,value 为位移,它会以 json 的形式持久化到磁盘 ${ROCKETMQ_HOME}/store/config/consumerOffset.json 文件中,具体格式如下:
{
"offsetTable": {
"test-topic@test-group": {
"0": 88526,
"1": 88528,
"2": 88532,
"3": 88537
}
}
}
